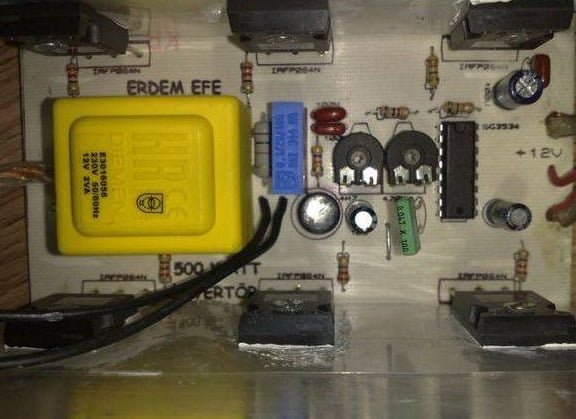
This project depicts a 250W PWM inverter circuit built around the IC SG3524. The SG3524 is an integrated switching regulator circuit with all the circuitry needed to build a single-ended regulator.
Moreover, the SG3524’s internal circuitry includes a pulse width modulator (PWM), oscillator, voltage reference, error amplifier, overload protection circuit, output drivers, and other components.
The SG3524 is at the heart of this PWM inverter circuit, which can compensate for variations in the output load.
A change in output load directly affects the output voltage in a non-PWM inverter (when output load increases, the output voltage decreases, and vice versa), but in a PWM inverter, the output voltage remains constant over a range of output load.
The Circuit Diagram.
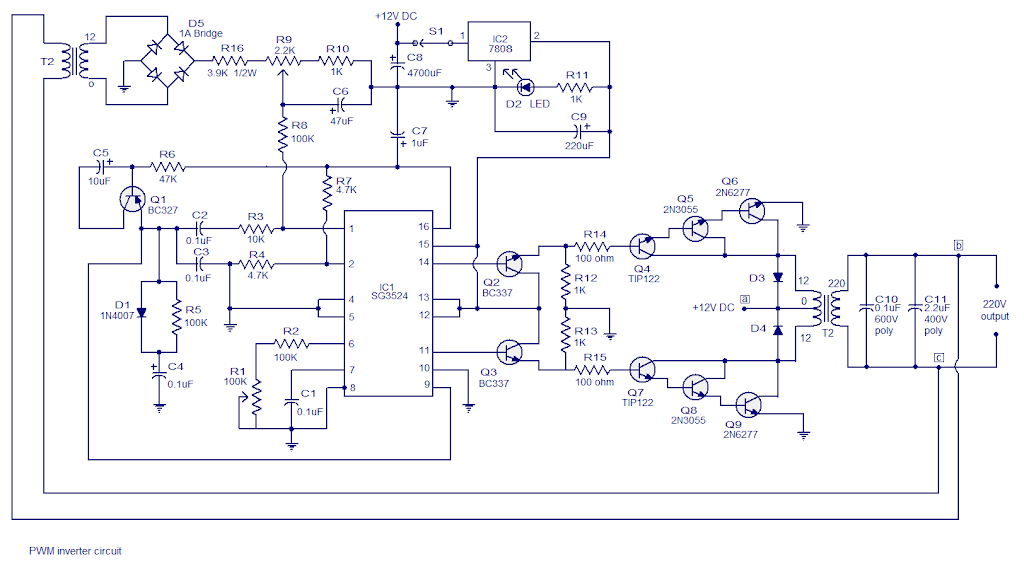
About the 250W PWM inverter circuit.
The frequency of the IC’s internal oscillator is set by resistor R2 and capacitor C1. The oscillator frequency can be fine-tuned using Preset R1.
Pins 14 and 11 are the emitter terminals of the IC’s internal driver transistor.
Also, check these related articles specially selected for you:
The driver transistor collector terminals (pins 13 and 12) are linked together and connected to the +8V rail (output of the 7808). Pin 14 and 15 of the IC provide two 50Hz pulse trains 180 degrees out of phase.
To produce 250W, the PMW signals drive the inverter’s transistor stages as follows. When the signal at pin 14 is high, transistor Q2 turns on, causing transistors Q4, Q5, and Q6 to turn on. Current flows from the +12V source (battery) connected at point a (marked with label a) through the upper half of the transformer (T1) primary and sinks to the ground via transistors Q4, Q5, and Q6.
This FM transmitter project also uses only transistors and works very well.
As a result of the electromagnetic induction, a voltage is induced in the transformer secondary, which contributes to the upper half cycle of the 220V output waveform.
Pin 11 will be low during this time, and the subsequent stages will be inactive. When IC pin 11 goes high, Q3 is turned on, so Q7, Q8, and Q9 are also turned on.
This 250W PWM inverter circuit causes current flows from the +12V source (labelled a) through the lower half of the transformer primary and sinks to the ground via transistors Q7, Q8, and Q9, and the induced voltage at the T2 secondary contributes to the lower half cycle of the 220V output waveform.
The inverter circuit’s output voltage regulation section operates as follows. The inverter output (T2 output) is tapped from points b and c and supplied to the transformer T2’s primary to obtain 250W. This emulates the PWM inverter circuit functionality.
This high voltage is stepped down by transformer T2, rectified by bridge D5, and this voltage (proportional to the inverter’s output voltage) is supplied to pin1 (inverting input of the IC’s internal error amplifier) via R8, R9, R16, and this voltage is compared with the internal reference voltage.
This error voltage is proportional to the output voltage deviation from the desired value, and the IC adjusts the duty cycle of the drive signals (at pins 14 and 12) to restore the desired output voltage.
Preset R9 can be used to adjust the inverter output voltage because it directly controls the amount of voltage fed back to the error amplifier section from the inverter output.
IC2 and its associated components generate an 8V supply from the 12V source to power the IC and its associated circuitries. Diodes D3 and D4 are freewheeling diodes that protect the driver stage transistors from voltage spikes caused by switching the transformer (T2) primaries.
In this 250W PWM inverter circuit, R14 and R15 limit the base current of Q4 and Q7. R12 and R13 are pulldown resistors for Q4 and Q7, preventing them from accidentally turning on. C10 and C11 are used to eliminate noise from the inverter output. C8 is a voltage regulator IC 7808 filter capacitor. R11 controls the current flowing through the indicator LED D2.
Notes.
- To get the best result from this 250W PWM inverter circuit, place the SG3524 in a holder or IC socket.
- Except for C10 and C11, all capacitors must be rated at least 15V.
- The inverter’s output voltage can be adjusted using Preset R9.
- Preset R1 can be used to change the operating frequency of the inverter.
- Heatsinks are required for transistors in the driver stage.
- T2 is a 1A transformer with a 220V primary and a 12V secondary.
- T1 is a 300VA transformer with a primary voltage of 12-0-12 V and a secondary voltage of 220V.
- Mica sheets must be used to isolate driver transistors from the heatsink.
These transistors’ mounting kits are widely available on the market. - The 7808 can be equipped with an optional finned aluminium heatsink.
- If a 1A bridge is not available to build this 250W PWM inverter circuit, construct one with four 1N4007 diodes.